The scope of the NIST Media Sanitization Guidelines is much more expansive than what was included in the legacy DoD data wiping standard. The Guidelines address how to set up a comprehensive system for creating policies, assigning responsibilities, determining risk tolerances, and informing decisions to sanitize or destroy data on a wide variety of media and devices. A short summary of applicable sanitization methods for various products is provided here.
This information is provided as a supplement to Cascade's 2016 IT Asset Disposition Trends and Best Practices benchmarking report. It serves as a brief overview of the NIST 800-88 Guidelines for Media Sanitization, which can be useful in defining and maintaining your own information destruction program.
| Types of data eradication methods in NIST |
The Guidelines establish three levels of data destruction that can be applied to different data storage devices. Organizations should pick the physical destruction of electronic sanitization method that meets their tolerance for risk. The destruction method may be different for each class of storage devices.
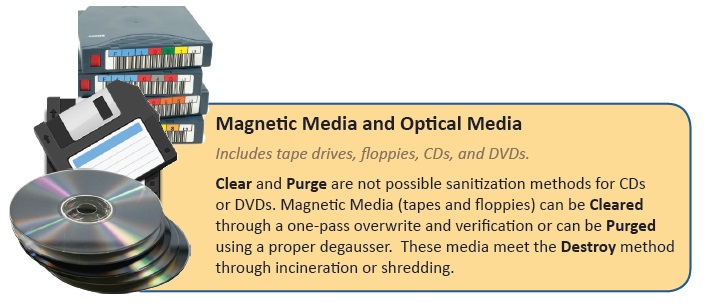
Clear is the method that uses software or hardware products to overwrite user-addressable storage space on media with non-sensitive data, when available. This is done by writing “0’s or 1’s” over all sectors in a drive or storage device. If this isn’t possible (such as in a basic cell phone or piece of office equipment), manufacturer resets and procedures that do not include rewriting might be the only option to Clear the device. Items that are Cleared may be able to be reused after they are sanitized.
Purge may be an overwrite, block erase, or Cryptographic Erase through the use of dedicated, standardized device sanitize commands that apply media-specific techniques to bypass the typical read and write commands. Items that are Purged may be able to be reused after they are sanitized.
Destroy is a physical process that makes data retrieval infeasible using state of the art laboratory techniques. Destruction methods include shredding, incineration, melting and pulverizing. Degaussing is also considered a destruction technique when used properly. Bending, cutting and drilling holes through a storage device are NOT considered destruction techniques. Destroyed items are not able to be reused. Demanufacturing followed by shredding or smelting is Cascade’s method for physical destruction.






The DoD 5220-22.M 3-pass wipe standard was originally published in 1995 in the National Industrial Security Program Operating Manual (NISPOM). In 2007, the Defense Security Service updated its “Clearing and Sanitization Matrix” and said, “DSS will no longer approve overwriting procedures for the sanitization or downgrading of IS storage devices.” The NIST Guidelines, originally published in 2006 and updated in 2014, are seen as a replacement to the legacy DoD standard.
Download our White Paper "Debunking the 3-pass overwrite requirement."


